Web Scraping
& HTML Parsing
Session 5
Extracting structured data from web pages using Python, BeautifulSoup, and XPath

2026 WayUp


What is Web Scraping?
Extracting data from regular web pages
Definition
Web Scraping is a technique for fetching and extracting data from web pages designed for human viewing, not machine consumption
No Standard Format
Unlike APIs, web pages lack a consistent structure for data representation
Unstable Source
Pages can change layout at any time, breaking your scraper
Last Resort
Use scraping only when no API is available
Web Scraping Workflow
From URL to DataFrame
Each step requires error handling—pages may be unavailable, structure may change, or elements may be missing
Understanding HTML
HyperText Markup Language
HTML Characteristics
- Markup language (like XML)
- Defines content structure and presentation
- Less strict than XML
- Browsers are fault-tolerant
Key Concept
Browsers highly tolerate errors in HTML
Without this tolerance, most websites wouldn't display properly
This makes HTML easier to write but harder to parse programmatically
HTML Structure Example
Opening and closing tags
<article class="product_pod">
<h3>
<a href="catalogue/book_1.html" title="A Light in the Attic">
A Light in...
</a>
</h3>
<p class="price_color">£51.77</p>
<p class="star-rating Three">
<i class="icon-star"></i>
</p>
</article>Elements
<article> | Container element |
<h3> | Heading level 3 |
<p> | Paragraph |
Targeting Strategies
- CSS Selectors:
.price_color - XPath:
//p[@class='price_color'] - Element attributes: class, id, title
DOM vs HTML Source
What you see is not what you get
Critical Distinction
What you see in browser DevTools is the rendered DOM (Document Object Model), not the raw HTML
Raw HTML
- What the server sends
- May contain errors
- What simple HTTP requests fetch
- Static content only
Rendered DOM
- Browser-corrected HTML
- JavaScript-modified content
- What you see in DevTools
- Dynamic, interactive
books.toscrape.com
A safe scraping sandbox
Perfect for Learning
books.toscrape.com - A fictional bookstore designed specifically for scraping practice
Stable Structure
HTML structure won't change unexpectedly
No JavaScript
All content loads in initial HTML
Rich Data
1000 books with titles, prices, ratings
Scraping-Friendly
No robots.txt restrictions
Scraping with BeautifulSoup
Python's most popular HTML parsing library
BeautifulSoup 4
User-friendly library for parsing HTML and navigating the document tree
Installation: pip install beautifulsoup4 requests
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# Fetch the web page
url = "http://books.toscrape.com"
response = requests.get(url)
# Parse HTML with BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.content, "html.parser")
# Find all book elements using CSS selectors
books = soup.select("article.product_pod")
# Extract data from each book
for book in books[:5]: # First 5 books
title = book.select_one("h3 a")["title"]
price = book.select_one(".price_color").text
print(f"{title}: {price}")XPath Alternative with lxml
More powerful but steeper learning curve
When to Use XPath
- Complex navigation patterns
- You're already familiar with XPath
- Need powerful filtering
- XML background
When to Use CSS Selectors
- Simple element selection
- You know CSS
- More readable code
- Web development background
from lxml import html
import requests
response = requests.get("http://books.toscrape.com")
tree = html.fromstring(response.content)
# XPath to select all book titles and prices
titles = tree.xpath("//article[@class='product_pod']//h3/a/@title")
prices = tree.xpath("//p[@class='price_color']/text()")
# Combine results
for title, price in zip(titles[:5], prices[:5]):
print(f"{title}: {price}")Exercise: Manual Data Extract
Sometimes manual is faster than automated
Your Challenge
Extract the Human Development Index table from Wikipedia as fast as possible
URL: Wikipedia HDI Page
1 Navigate
Open the Wikipedia page
2 Inspect
Find the HDI table in the page
3 Extract
Use ANY technique: copy-paste, scraping, browser tools
4 Save
Produce a CSV file
Limits of Direct HTML Fetching
When simple requests aren't enough
The JavaScript Problem
Many modern websites load content dynamically using JavaScript after the initial page load
Static Content
Works with: requests + BeautifulSoup/lxml
- HTML rendered server-side
- Content in initial response
- No JavaScript required
- Example: books.toscrape.com
Dynamic Content
Requires: Headless browser (Selenium, Playwright)
- JavaScript execution needed
- Content loads after page render
- Simulates real browser behavior
- Example: Most modern SPAs
When to Use Web Scraping?
Cost-benefit analysis
Short Answer
When you cannot do otherwise - Scraping should be your last resort, not your first choice
Good Use Cases
- No API available
- Large volume of data
- Static content (rarely changes)
- Reference data extraction
Beware
- Ongoing maintenance costs
- Breaks when site changes
- Legal/ethical considerations
- Rate limiting and blocking
1 Check for API
Always look for official data access first
2 Assess Volume
Is automation worth the development time?
3 Consider Manual
Small datasets might be faster to copy-paste
4 Plan Maintenance
Budget time for fixing broken scrapers
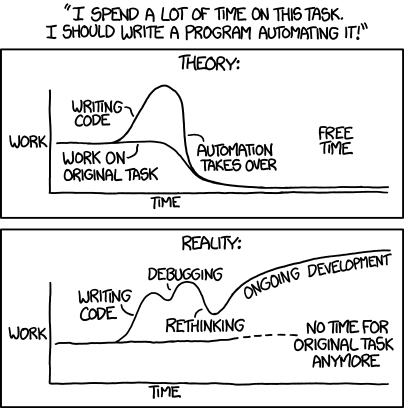
Automation: Theory vs Reality
The classic XKCD truth about automation
Integrating Scraped Data with Orange
From web pages to data tables
Use the Python Script widget to scrape and convert to Orange tables
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from Orange.data import Table, Domain, StringVariable, ContinuousVariable
# Scrape book data
response = requests.get("http://books.toscrape.com")
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.content, "html.parser")
# Extract data from each book
data = []
for book in soup.select("article.product_pod"):
title = book.select_one("h3 a")["title"]
# Remove £ symbol and convert to float
price = float(book.select_one(".price_color").text[1:])
data.append([title, price])
# Create Orange table
domain = Domain([StringVariable("title")], [ContinuousVariable("price")])
out_data = Table.from_list(domain, data)Exercise: Scrape and Analyze Books
Multi-page scraping challenge
Your Challenge
Scrape books from multiple pages and analyze patterns
1 Multi-Page
Scrape first 3 pages of books.toscrape.com
2 Extract Fields
Title, price, star rating (1-5)
3 Orange Table
Create table with all extracted data
4 Visualize
Price distribution, rating vs price
Bonus Challenge
Handle pagination automatically by following "next" links programmatically
Better Alternatives to Web Scraping
Structured data sources
Remember
REST APIs and XML files are almost always better than web scraping when available
Why APIs Are Better
- Documented structure
- Stable, versioned endpoints
- Rate limiting is clear
- Legal terms defined
- Error handling built-in
Explore More
- Continue to REST API exercises
- Continue to XML parsing
- Check if the site offers data exports
- Contact site owners for data access
Key Takeaways
1
Last resort only. Web scraping is fragile and high-maintenance. Always check for APIs or data exports first.
2
DOM ≠ HTML source. JavaScript-rendered content requires headless browsing, not simple HTTP requests.
3
Cost-benefit matters. Small datasets might be faster to extract manually than to automate.
4
BeautifulSoup or lxml. Choose based on familiarity—CSS selectors (BS4) or XPath (lxml).