Advanced Java
JPA & Hibernate
Master Object-Relational Mapping

What is JPA?
Java Persistence API (JPA) is a specification for Object-Relational Mapping (ORM)
JPA is:
- A specification not an implementation
- A standard for mapping Java objects to database tables
- Part of Jakarta EE (formerly Java EE)
JPA is NOT:
- A database
- A framework by itself
- Limited to one database vendor
Why JPA?
Without ORM:
- Manual JDBC connection management
- Mix of SQL and Java code
- Database-specific SQL
- Manual ResultSet to Object conversion
- Lots of boilerplate code
With JPA:
- Automatic connection and transaction management
- Database-agnostic queries (JPQL)
- Automatic object mapping
- Less code, more productivity
JPA Implementations
Several implementations exist:
| Implementation | Description |
|---|---|
| Hibernate | Most popular, feature-rich |
| EclipseLink | Reference implementation |
| OpenJPA | Apache project |
We'll use Hibernate - the most widely adopted ORM framework
Setting Up JPA with Spring Boot
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresql</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency># application.properties
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/mydb
spring.datasource.username=user
spring.datasource.password=password
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQLDialect
Creating Your First Entity
@Entity
@Table(name = "users")
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(name = "email", nullable = false, unique = true)
private String email;
@Column(name = "full_name", length = 100)
private String fullName;
@Column(name = "created_at")
private LocalDateTime createdAt;
// Constructors, getters, setters
}JPA Annotations Explained
@Entity- Marks class as JPA entity@Table- Specifies table name (optional if class name matches)@Id- Marks primary key field@GeneratedValue- Auto-generate primary key@Column- Maps field to column (optional with customization)
Generation Strategies:
AUTO- Let JPA chooseIDENTITY- Database auto-incrementSEQUENCE- Database sequenceTABLE- Separate table for ID generation
One-to-Many Relationship
@Entity
public class Author {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String name;
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "author", cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
private List<Book> books = new ArrayList<>();
}
@Entity
public class Book {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String title;
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name = "author_id")
private Author author;
}Many-to-Many Relationship
@Entity
public class Student {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String name;
@ManyToMany
@JoinTable(
name = "student_course",
joinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "student_id"),
inverseJoinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "course_id")
)
private Set<Course> courses = new HashSet<>();
}
@Entity
public class Course {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String name;
@ManyToMany(mappedBy = "courses")
private Set<Student> students = new HashSet<>();
}Cascade Types
Control how operations propagate to related entities:
| Cascade Type | Description |
|---|---|
| PERSIST | Propagate persist operation |
| MERGE | Propagate merge operation |
| REMOVE | Propagate remove operation |
| REFRESH | Propagate refresh operation |
| DETACH | Propagate detach operation |
| ALL | All of the above |
Fetch Strategies
LAZY Loading (Default for collections):
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "author", fetch = FetchType.LAZY)
private List<Book> books;Data loaded only when accessed
EAGER Loading (Default for single entities):
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.EAGER)
private Author author;Data loaded immediately with parent entity
Best Practice: Use LAZY by default, load eagerly only when needed
Spring Data JPA Repository
No need to write implementation code!
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
// Spring Data generates implementation automatically
// Query methods by convention
User findByEmail(String email);
List<User> findByFullNameContaining(String name);
List<User> findByCreatedAtAfter(LocalDateTime date);
@Query("SELECT u FROM User u WHERE u.email LIKE %:domain")
List<User> findByEmailDomain(@Param("domain") String domain);
// Pagination and sorting
Page<User> findAll(Pageable pageable);
}Repository Hierarchy
Repository<T, ID>- Marker interfaceCrudRepository<T, ID>- Basic CRUD operationsPagingAndSortingRepository<T, ID>- Adds pagination and sortingJpaRepository<T, ID>- JPA-specific extensions
JpaRepository adds:
- Batch operations (
saveAll,deleteInBatch) - Flushing persistence context
- Query by example
Query Method Keywords
| Keyword | Example |
|---|---|
| findBy... | findByEmail(String email) |
| And, Or | findByNameAndEmail(String name, String email) |
| Between | findByCreatedAtBetween(LocalDateTime start, LocalDateTime end) |
| LessThan, GreaterThan | findByAgeGreaterThan(int age) |
| Like, Containing | findByNameContaining(String name) |
| OrderBy | findByAgeOrderByNameAsc(int age) |
Custom Queries with @Query
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
// JPQL
@Query("SELECT u FROM User u WHERE u.email LIKE %:domain")
List<User> findByDomain(@Param("domain") String domain);
// Native SQL
@Query(value = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE created_at > ?1",
nativeQuery = true)
List<User> findRecentUsers(LocalDateTime date);
// Modifying queries
@Modifying
@Query("UPDATE User u SET u.active = false WHERE u.lastLogin < :date")
int deactivateInactiveUsers(@Param("date") LocalDateTime date);
// DTOs / Projections
@Query("SELECT new com.example.dto.UserDTO(u.id, u.email) FROM User u")
List<UserDTO> findAllUserDTOs();
}Pagination and Sorting
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
public Page<User> getUsers(int page, int size) {
Pageable pageable = PageRequest.of(page, size,
Sort.by("fullName").ascending());
return userRepository.findAll(pageable);
}
public List<User> getTopUsers(int count) {
Pageable pageable = PageRequest.of(0, count);
return userRepository.findAll(pageable).getContent();
}
}Entity Lifecycle
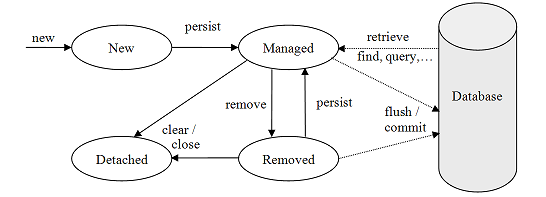
- Transient: New object, not associated with persistence context
- Managed: Associated with persistence context, changes tracked
- Detached: Was managed, but no longer in persistence context
- Removed: Marked for deletion
Transaction Management
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Transactional
public void createUser(User user) {
userRepository.save(user);
// Any exception rolls back the transaction
}
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public User findUser(Long id) {
return userRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new UserNotFoundException(id));
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public void createUserInNewTransaction(User user) {
userRepository.save(user);
// Always executes in new transaction
}
}The N+1 Problem
The Problem:
// 1 query to get all authors
List<Author> authors = authorRepository.findAll();
// N queries - one for each author's books!
for (Author author : authors) {
System.out.println(author.getBooks().size());
}The Solution:
// Use JOIN FETCH to load everything in one query
@Query("SELECT a FROM Author a LEFT JOIN FETCH a.books")
List<Author> findAllWithBooks();
// Or use @EntityGraph
@EntityGraph(attributePaths = "books")
List<Author> findAll();Performance Best Practices
1. Use Appropriate Fetch Strategy
- Default to LAZY loading
- Use JOIN FETCH for specific queries
2. Batch Operations
// Good - batch insert
userRepository.saveAll(users);
// Bad - multiple individual inserts
for (User user : users) {
userRepository.save(user);
}3. Use Projections
// Load only needed fields
public interface UserProjection {
Long getId();
String getEmail();
}
List<UserProjection> findAllProjectedBy();Second-Level Cache
Add Hibernate second-level cache with Ehcache:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-ehcache</artifactId>
</dependency>spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache=true
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.cache.region.factory_class=org.hibernate.cache.ehcache.EhCacheRegionFactory@Entity
@Cacheable
@org.hibernate.annotations.Cache(usage = CacheConcurrencyStrategy.READ_WRITE)
public class User { }Database Migration with Flyway
<dependency>
<groupId>org.flywaydb</groupId>
<artifactId>flyway-core</artifactId>
</dependency>Create migration files in src/main/resources/db/migration/:
db/migration/
├── V1__create_users_table.sql
├── V2__add_email_index.sql
└── V3__create_orders_table.sql-- V1__create_users_table.sql
CREATE TABLE users (
id BIGSERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
email VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL UNIQUE,
full_name VARCHAR(100),
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);Auditing
Automatically track who created/modified entities and when:
@Configuration
@EnableJpaAuditing
public class JpaConfig { }
@MappedSuperclass
@EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class)
public abstract class Auditable {
@CreatedDate
private LocalDateTime createdDate;
@LastModifiedDate
private LocalDateTime lastModifiedDate;
@CreatedBy
private String createdBy;
@LastModifiedBy
private String lastModifiedBy;
}
@Entity
public class User extends Auditable {
// User fields
}Exercise 1: Create Entity Model
Task: Design a blog application data model
Requirements:
- Create User entity (id, username, email, password)
- Create Post entity (id, title, content, createdAt)
- Create Comment entity (id, text, createdAt)
- Add One-to-Many: User → Posts
- Add One-to-Many: Post → Comments
- Add Many-to-One: Comment → User
- Add appropriate indexes
Exercise 2: Repository Queries
Task: Implement complex queries
Requirements:
- Find posts by author username
- Find posts created in date range
- Find posts with comments count > 10
- Find top 10 most commented posts
- Implement pagination for posts
- Create custom DTO projection
Exercise 3: Optimize Performance
Task: Identify and fix N+1 queries
Requirements:
- Enable SQL logging
- Find N+1 query problems
- Fix with JOIN FETCH or @EntityGraph
- Implement second-level cache
- Add database migration with Flyway
- Measure performance improvements
Common Pitfalls
1. Open Session in View (OSIV)
Disabled by default in Spring Boot 2+
spring.jpa.open-in-view=false2. Missing @Transactional
Always use @Transactional for write operations
3. Lazy Loading Exceptions
Fetch data within transaction or use DTOs
4. Too Many Queries
Monitor SQL with show-sql=true
Summary
In this module, you learned:
- ✓ JPA fundamentals and architecture
- ✓ Entity mapping and relationships
- ✓ Spring Data JPA repositories
- ✓ Query methods and custom queries
- ✓ Transaction management
- ✓ Performance optimization techniques
- ✓ Database migrations
Next Module: RESTful Web Services & APIs
Resources
- JPA Specification: jakarta.ee/specifications/persistence
- Hibernate Documentation: hibernate.org/orm/documentation
- Spring Data JPA: docs.spring.io/spring-data/jpa
- Baeldung JPA Tutorials: baeldung.com/learn-jpa-hibernate
- Flyway Documentation: flywaydb.org/documentation